Registration required: October 13, 2022 7:00pm – 9:00pm Pacific Time
Co Leader – Reflexivity: The Cybersecurity Superpower You Haven’t Met Yet – Humble Science, PBLLC

Building upon industries’ general understanding of the current state of artificial intelligence, we explore indicators that reveal a wide range of algorithmic maturity throughout the entire ecosystem, including the cloud, IoT, supply chain, and the varied and various X-as-a-Service (Xaas) providers. As a result, threat landscape is expanding exponential into virtual and non-terrestrial spaces, forever blurring traditional protect surface boundaries. How did we get here and what are the critical skills required to build cybersecurity teams of the future? Learn the five key skillsets that will offset tomorrow’s threat landscape, and how to implement pragmatic solutions today so as to ensure agility and foresight capacities JIT.
About Humble Science, PBLLC
Pursuant to §§ 18-1202(a)-(b) of the Act, the LLC shall provide systemic, novel, and sustainable society-valued growth strategies and solutions to public and private stakeholders of the digital economy. In this era of data-driven intelligence, the LLC commits to approaching these uncharted areas of science with epistemic humility while striving to free the historically marginalized from unconquered systems of oppression. The LLC shall strive to strengthen the emerging digital economy—and its various markets—with checks and balances that incentivize positive-sum market innovation and a public return on public investments. The LLC shall have a positive effect on the centering of humanity in the exploration and discovery of sustainable artificial intelligence and quantum technologies capable of affecting the human condition at scale—with special emphasis on the economic, social and environmental challenges affecting the world’s poorest people.
Co Topic Leader – Legislation Related to Artificial Intelligence and the Lag in Ethics & Compliance Guidance for Implementation of Necessary Controls – Our Training Journey for AI/ML

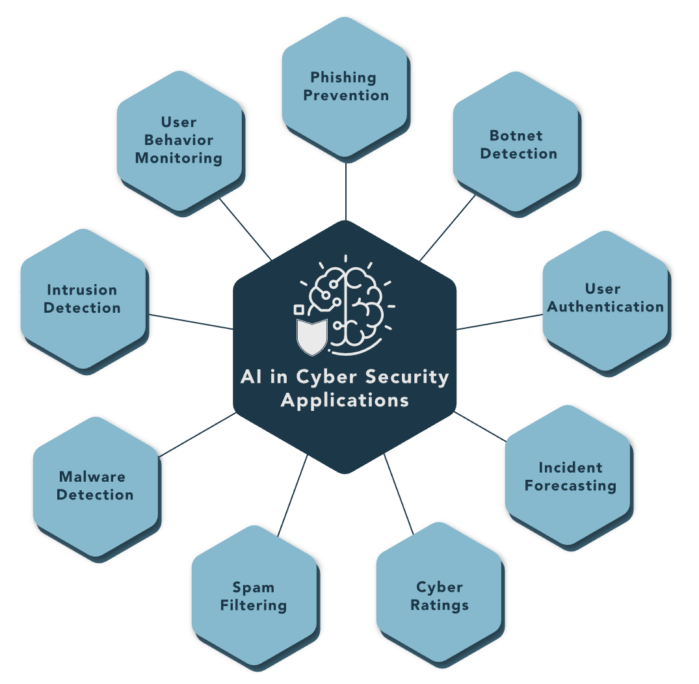
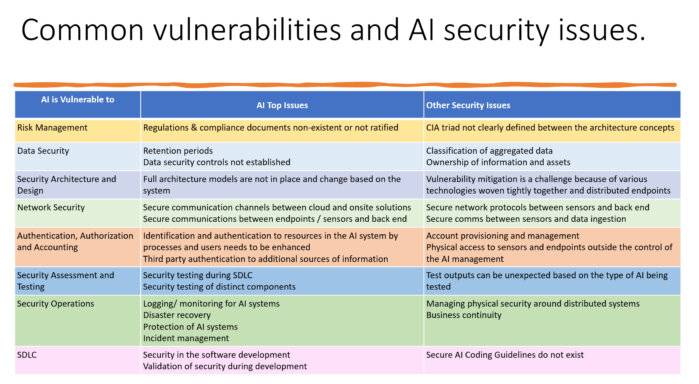
Cybersecurity professionals understand the many benefits and potential for Artificial intelligence (AI) security defense systems. The obvious concerns about potential misuse or unintended consequences of AI, however, have prompted efforts to examine and develop standards, such as the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) initiative involving workshops and discussions with the public and private sectors around the development of federal standards to create building blocks for reliable, robust, and trustworthy AI systems. State lawmakers must evaluate AI benefits against their potential for harm. This hour covers a summary of some of the State level initiatives, with emphasis to our State of California, and asks how we as cybersecurity professionals balance what we monitor, what we learn, and what we protect (CIA), and how we advise our clients as they acquire and implement increasingly AI dependent processes and technology.
About EnterpriseGRC Solutions Inc.
EnterpriseGRC Solutions is a Governance Risk and Compliance company specializing in mapping cloud security and cyber security frameworks. We implement governance, ISMS, Risk Frameworks, and compliance automation products and programs. We emphasize system-based policies specific to security settings for secure configuration management. EnterpriseGRC is a women-owned small business offering compliance readiness, Security & GRC tools, Enterprise Security Architecture, Cybersecurity Risk Assessment, and a wide variety of resources for security and GRC technology support.
Our Guest Moderators and Future Speakers – Future Topics involving Data Science, Critical Thinking and Predictive Analysis


ISC2 offers three Professional Development Institute courses on the topic of AI. After several months of collaborating together, Jodi Masters-Gonzalves and I (Robin Basham) decided that whatever we present to the ISC2 East Bay community should align with content authorized for study by our parent organization. To access the full courses, go to Cybersecurity Certification Training | Exam Prep (isc2.org)

Resources list
These resources are mentioned during tonight’s presentation.
eCFR :: 16 CFR Part 312 — Children’s Online Privacy Protection Rule
Towards a Standard for Identifying and Managing Bias in Artificial Intelligence (nist.gov)
The Malicious Use of Artificial Intelligence: Forecasting, Prevention, and Mitigation. Brundage, M. et al. (2018, February). Future of Humanity Institute. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1802/1802.07228.pdf
The Ethics Certification Program for Autonomous and Intelligent Systems (ECPAIS)
The goal of The Ethics Certification Program for Autonomous and Intelligent Systems (ECPAIS) is to create specifications for certification and marking processes that advance transparency, accountability and reduction in algorithmic bias in Autonomous and Intelligent Systems (AIS).
The value of this certification process in the marketplace and society at large cannot be underestimated. The proliferation of systems in the form of smart homes, companion robots, autonomous vehicles or any myriad of products and services that already exist today desperately need to easily and visually communicate to consumers and citizens whether they are deemed “safe” or “trusted” by a globally recognized body of experts providing a publicly available and transparent series of marks.
Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS)
IEEE 7000™-2021 integrates ethical and functional requirements to mitigate risk and increase innovation in systems engineering product design and utilizes “Value-based Engineering” as its core methodology providing ways to elicit, conceptualize, prioritize and respect end user values in system design.
Global Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS) Well-Being Initiative
The IEEE Applied Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS) Risk and Impact Framework Initiative
Trusted Data and Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS) Playbook for Finance Initiative
Developing an interoperable data infrastructure through extensible governance and metadata lifecycle framework
Helping to advance individual and community-level prosperity; socially, politically, and economically
Artificial Intelligence Systems Archives – IEEE Standards Association
The IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems
ISO/IEC from ISO.ORG
- ISO/IEC 23053:2022 – Framework for Artificial Intelligence (AI) Systems Using Machine Learning (ML)
- ISO 9241-110:2020 – Ergonomics of human-system interaction — Part 110: Interaction principles
- ISO/TR 22100-5:2021 – Safety of machinery — Relationship with ISO 12100 — Part 5: Implications of artificial intelligence machine learning
- ISO/IEC 22989:2022 – Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Artificial intelligence concepts and terminology
- ISO/TR 24291:2021 – Health informatics — Applications of machine learning technologies in imaging and other medical applications
- ISO/IEC TR 24030:2021 – Information technology — Artificial intelligence (AI) — Use cases
- ISO/IEC 38507:2022 – Information technology — Governance of IT — Governance implications of the use of artificial intelligence by organizations
- ISO/TR 9241-810:2020 – Ergonomics of human-system interaction — Part 810: Robotic, intelligent, and autonomous systems
- ISO/TS 5346:2022 – Health informatics — Categorial structure for the representation of traditional Chinese medicine clinical decision support system
- ISO/IEC TR 24368:2022 – Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Overview of ethical and societal concerns
- ISO/IEC TR 24372:2021 – Information technology — Artificial intelligence (AI) — Overview of computational approaches for AI systems
- ISO/IEC TR 24027:2021 – Information technology — Artificial intelligence (AI) — Bias in AI systems and AI aided decision making
- ISO/IEC TR 24028:2020 – Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Overview of trustworthiness in artificial intelligence
- ISO/IEC TR 24029-1:2021 – Artificial Intelligence (AI) — Assessment of the robustness of neural networks — Part 1: Overview
EU
Twitter Research
Introduction to Twitter data processing and storage on AWS – DEV Community 👩💻👨💻
Amazon Training
Discovering Hot Topics Using Machine Learning | Implementations | AWS Solutions (amazon.com)
One of many resources shared by Brian Barnier
https://www.illumeo.com/courses/artificial-intelligence-when-it-awesome-when-it-hazardous
Terms necessary to passing the three ISC2 PDI
Algorithms are processes for solving mathematical operations. In the field of computer programming, algorithms are used to define a set of processes that the program must take to determine outcomes.
Cognitive computing refers to the science of teaching a system how to comprehend problems, like a human, to find solutions in complex situations where not all the data gets incorporated into the data model. Present in many AI applications, cognitive computing, like VR, robotics, and neural networks helps to extrapolate situations and possible solutions by the program and system.
Natural language processing is a field within computer science that studies the interaction between humans and computers for verbal communication. This science focuses on understanding and processing syntax, semantics, speech, and dialogue, to name a few.
Visual Information Processing describes the ability of a system or program to understand and translate information gained by optical sensors in the visual and non-visual spectrums (ultraviolet and Infrared). This information translates to data that can be processed by the application to make decisions based on this type of data.
Supervised learning is an algorithm that analyzes data and returns the desired output. This is done by taking input and analyzing it with expected and pre-defined input-output data and defining the expected outputs of that data pair. The algorithm then infers the best (most reasonable) course of action based on the training data it possesses.
Unsupervised learning is an algorithm characterized by self-organizing unknown patterns in data pairs to model the probabilities and the outcomes based on the availability of the data. The model gets more precise, with more data.
Reinforcement learning is an algorithm that focuses not on the input/output pairs but on the outcomes that bring the best reward. Think positive reinforcement, without losing the “incorrect/not best” results.
Autonomic computing refers to an area of study in which systems and programs can self-correct and react to unexpected changes. This course of study was started by IBM in 2001 to help computer systems self-manage themselves when errors occurred.
Chatbots are artificial intelligence programs designed to carry out conversations and interact with a human via text or voice. These programs are designed to simulate how a human would speak or type, some are simple (like you see on websites), and some can be as complex as to attempt to pass the Turing test.
Data mining is the way programs discover patterns in large data sets. Data mining is a cross between computer science and statistics, to extract information and transform the information into an understandable structure for further use. Data mining is a buzzword and is usually used to describe the collection, extraction, warehousing, analysis, and statistics of data.
Predictive analysis describes the analytics performed on a data set to make predictions about future events. These analytics make use of data mining, statistics, and modeling. For example, the National Weather Service uses weather predicting models to provide weather forecasts around the country.
A note from our Director of Education, Jack K Rasmus-Vorrath
Initiatives
Google Spaces: Sign-up
-Chapter Info, Seminar Discussion, Group Chat,
-Certification Info, Training Resources,
– CISSP Study Group, New Literature, Security News
CISSP Study Sessions
-Coming Soon: education@isc2-eastbay-chapter.org
»Spotlight
–“See Yourself in Cyber”
•(ISC)2 1M Certified in Cybersecurity



